What Is a Phylogenetic Species Concept?
The phylogenetic species concept is the concept of species having a common ancestor with unique evolutionary history. Such types of species possess certain defined and derived traits or sometimes a combination of such traits that are absent in other members of species.
In contrast to the biological species concept, breeding between organisms of different species does not pose a big problem in these species. And, therefore, this concept of species is less restrictive than biological species.
The phylogenetic species concept also defines those species that have evolved with continuity of sexual fertility but in an unbroken line of descent. Thus, it implies knowledge of whether or not regular interbreeding occurs between populations.
Phylogenetics is the scientific discipline that deals with phylogeny. Whereas phylogeny is the study of the evolutionary history of different species. And, thus it studies phylogenetic species.
Identification of Phylogenetic Species
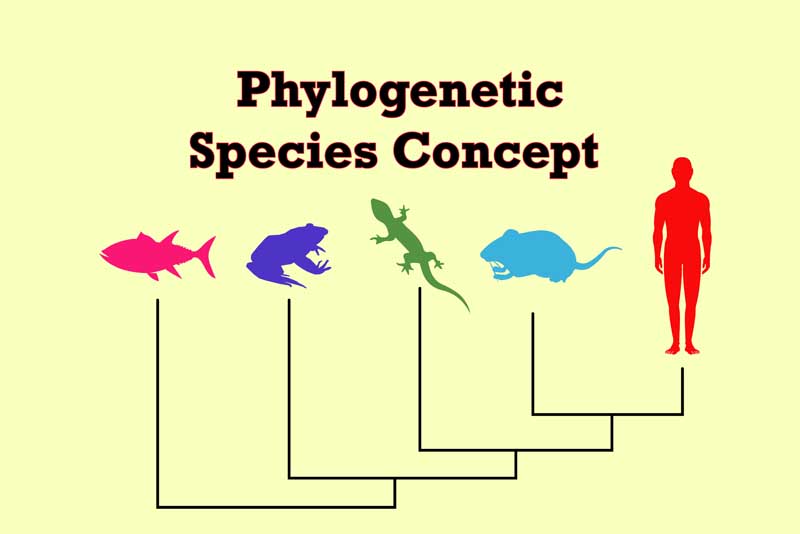
According to the evolutionary pattern of relationships, such species are usually expressed in the pattern of a binary branching tree also commonly known as phylogenetic tree.
However, if hybridization produces new lineages, common in many plants and some animals, then it is called ‘‘reticulate.’’
Phylogenies are estimated by using phenetics, parsimony, or other statistical and analytical methods. And, a competing phylogenetic species concept (PSC) also evaluates from this vantage.
However, there are two major analytical approaches that are common in determining the composite phylogenetic information within the hereditary pathways of a pedigree.
The first one is consensus phylogenetic trees across allelic transmission routes, and secondly, composite phonograms from quantitative values of organismal ancestry.
However, the outcomes of both these approaches express that there is no sharp distinction between phylogenetic and biological species.
And, the difference between these two concepts is illusory. Moreover, the historical descent and reproductive ties are relating to aspects of phylogeny and jointly illuminate biotic discontinuity.
Advantages
There are several advantages of the phylogenetic species concept. as, it can recognize the role of history in producing species explicitly, distinctly, and can reasonably objective.
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree) is a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities on the basis of similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
All life on this planet relates to a single phylogenetic tree, and that indicates the common ancestry.
However, in a rooted phylogenetic tree, each node with descendants represents the most recent common ancestor of those descendants. While, the edge lengths in some trees may interpret as time estimates.
Each node is called a taxonomic unit. And, the internal nodes are usually known as hypothetical taxonomic units, which are not directly observable.
Such types of trees are useful in fields of biology such as bioinformatics, systematics, phylogenetics and many others.
On the other hand, unrooted trees only demonstrate the relation of leaf nodes and do not require the ancestral root to be inferred.
Disadvantages
The primary disadvantage of this concept is that, currently, phylogenies are available for only a small set of populations. As, critics analyze that it would lead to recognition of numerous other species than other species concept.
However, the basic disadvantage is too many decisions on how much difference between individuals is too much variation. And, almost all populations are different from one another as they contain non-identical individuals.
What Is the Limitation of The Phylogenetic Species Concept?
The main limitation of it is that the evolutionary histories have been portrayed for moderately few bunches of life forms, so scientists are not however able to apply the phylogenetic species concept to all forms of life.
Evolutionary species are apparent and it can use on any species.
The good species of this kind are rare and they cannot recognize pharaphylatic species group.
Example
For Instance, the A and B lineages of Ensatina Salamander are two separate species. While, each lineage shares a common ancestor that members of other species do not. And, according to phylogenetic species, even it diversifies a lot that Lineage C is a separate specie.
Summary
Phylogenetics is a scientific discipline that concerns phylogeny. And, phylogeny describes the evolutionary history of different species, including biological and phylogenetic species.
Phylogenetic species are different from biological species, as they have distinct characteristics and also share a single ancestor.
Previously, this concept of species is considered quite different from the biological species concept. However, later on, several analytical approaches prove no prominent distinction between these two concepts.